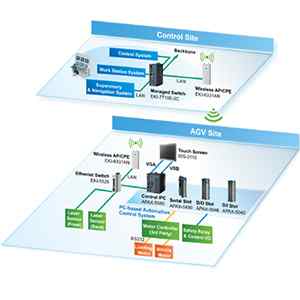
SCADA Systems: Monitoring and Control in Plant Automation

Introduction:
In the intricate tapestry of industrial processes, the significance of efficient monitoring and control cannot be overstated. At the core of every successful manufacturing endeavor lies the ability to oversee and regulate operations in real-time, ensuring precision, reliability, and optimal performance. As industries evolve and embrace the era of smart manufacturing, the role of advanced technologies becomes increasingly crucial. One such technological linchpin that coordinates the flow of control and data acquisition is SCADA, standing tall as a beacon of efficiency in the realm of plant automation.
Monitoring and Control in Industrial Processes: The dynamic landscape of industrial processes demands a meticulous balance between various parameters to achieve seamless production. Whether it's ensuring the right temperature in a chemical reactor or precisely managing the flow of materials in an assembly line, the ability to monitor and control each facet is pivotal. Timely interventions, data-driven decision-making, and real-time adjustments are the keystones that not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to the overall quality and safety of the end product.
Introduction to SCADA Systems:
Within the intricate interplay of industrial dynamics, SCADA emerges as a technological virtuoso. SCADA, denoting Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, assumes the role of a central nervous system, providing a holistic solution for monitoring, data collection, and control in industrial processes. Its sophisticated architecture, featuring Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), and Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs), serves as a bridge connecting the physical components of a plant with the operators at the helm of operations.
As industries continue their journey into the era of automation, SCADA systems stand as sentinels, facilitating a seamless integration of various components. From visualizing real-time data to enabling remote control, SCADA plays a pivotal role in augmenting the efficiency, reliability, and safety of industrial operations. In the pages that follow, we delve into the core of SCADA systems, unraveling their components, exploring their capabilities, and understanding how they contribute to the tapestry of modern plant automation.
Section 1: Understanding SCADA Systems
Within the domain of industrial automation, SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems stand as crucial coordinators, seamlessly intertwining the complex elements of control and data acquisition. Fundamentally, a SCADA system is identified by its capability to supervise, collect data, and exercise control over a wide array of industrial processes.
The components that form the backbone of SCADA include Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), tasked with gathering data from field devices; Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), acting as the nerve center for control functions; and the Human Machine Interface (HMI), providing a visual gateway for operators to interact with the system. This triad of components operates in concert, creating a robust architecture that facilitates the seamless monitoring and control of industrial processes.
The communication protocols utilized in SCADA systems are crucial for facilitating the exchange of data among these components, guaranteeing a prompt and precise flow of information. This section extensively explores the detailed design and functionality of SCADA systems, revealing the collaboration between RTUs, PLCs, and HMI, while elucidating the communication protocols that form the foundation of their cohesive operation.
Section 2: Key Features and Capabilities:
The prowess of SCADA systems extends far beyond their architectural composition, manifesting in a rich tapestry of features and capabilities that redefine the landscape of industrial automation. At the forefront is real-time monitoring, a hallmark of SCADA's functionality.
Through a sophisticated network of sensors and devices, SCADA enables the instantaneous collection and presentation of data, affording operators an unobstructed view into the inner workings of plant processes. This real-time insight not only enhances decision-making but also serves as the bedrock for proactive adjustments, ensuring optimal performance.
Data acquisition, another integral facet, involves the meticulous collection of information from a myriad of sensors and devices scattered throughout the industrial landscape. SCADA's ability to seamlessly aggregate this data provides a comprehensive understanding of process variables, fostering precision and reliability in manufacturing operations.
Alarm and event management emerge as vigilant guardians. SCADA systems are equipped with robust mechanisms that swiftly identify anomalies or critical situations. Through timely alerts and notifications, operators are empowered to respond promptly, mitigating potential risks and maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process.
The paradigm of remote control and operation represents a pinnacle of SCADA's capabilities. With operators stationed at a central location, SCADA facilitates remote oversight and manipulation of industrial processes. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also minimizes the need for physical intervention, especially in environments where accessibility may be challenging. This section delves into the intricacies of these key features, unraveling how real-time monitoring, data acquisition, alarm management, and remote control converge to empower industries in their pursuit of heightened efficiency and control.
Section 3: Integration with Plant Automation:
In modern industrial automation, SCADA systems emerge not as standalone virtuosos but as collaborative conductors, seamlessly integrating with diverse automation systems to harmonize the entire ensemble. SCADA's compatibility with other automation systems, such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS), forms a cornerstone of its capabilities. This interoperability facilitates a cohesive ecosystem where data flows seamlessly between components, creating a unified platform for comprehensive control and monitoring.
Beyond traditional automation components, SCADA extends its reach to embrace the era of Industry 4.0 by playing a pivotal role in integrating industrial robots and smart devices. As robotic arms gracefully move through manufacturing processes and smart devices contribute to the influx of real-time data, SCADA acts as the unifying force that coordinates their collaboration. The result is a synchronized industrial landscape where human-machine cooperation becomes not just a possibility but a reality.
SCADA makes a paramount contribution to plant automation by elevating efficiency and reducing downtime through smooth integration. Offering a centralized interface for monitoring and control, SCADA optimizes workflows, streamlines processes, and enables swift responses to dynamic production challenges. This section explores the nuanced coordination of compatibility, collaboration, and cohesion, demonstrating how SCADA's integration capabilities drive industries toward a future characterized by heightened efficiency and resilience.
Section 4: Benefits of SCADA Systems:
The adoption of SCADA systems in industrial landscapes yields a myriad of transformative benefits, each contributing to the overarching goal of operational excellence. Foremost among these advantages is the marked improvement in efficiency and productivity. By providing real-time insights, enabling swift decision-making, and facilitating remote control, SCADA systems empower industries to streamline processes and enhance overall operational effectiveness.
The commitment to data accuracy and reliability stands as another hallmark of SCADA's impact. Through meticulous data acquisition and monitoring, SCADA ensures that the information guiding operational decisions is not only timely but also precise, fostering a foundation of trust in the integrity of the data-driven processes.
A tangible outcome of deploying SCADA systems is the reduction in operational costs. The optimized workflows, proactive maintenance enabled by real-time monitoring, and the minimization of downtime collectively contribute to a leaner and more cost-effective operational model.
Section 5: Challenges and Solutions:
As SCADA systems ascend to the forefront of industrial automation, they encounter a spectrum of challenges that necessitate vigilant attention and innovative solutions. Chief among these challenges are security concerns that loom over SCADA systems, given their role as central orchestrators of critical infrastructure. This section addresses the nuanced landscape of cybersecurity in SCADA, exploring strategies to fortify these systems against potential threats and ensuring the resilience of operations.
Ensuring data integrity and system reliability emerges as a pivotal concern, as the accuracy of decisions hinges on the quality of the underlying data. Delving into this challenge, the discussion spans the implementation of data validation mechanisms, redundancy strategies, and continuous monitoring protocols to safeguard the integrity of the data flowing through SCADA systems.
Navigating the intricate terrain of SCADA challenges requires strategic foresight and proactive measures. This section concludes by unraveling a repertoire of strategies for overcoming common challenges. From adopting robust encryption methods to implementing regular system audits and employee training, these strategies collectively contribute to the fortification of SCADA systems, transforming challenges into opportunities for continuous improvement and resilience.
Section 6: Future Trends in SCADA Systems:
As we peer into the future of industrial automation, the trajectory of SCADA systems unfolds with a tapestry woven from the threads of cutting-edge advancements. A prominent trend shaping this future is the seamless integration of SCADA with the Internet of Things (IoT) and the principles of Industry 4.0. This convergence propels SCADA beyond traditional boundaries, ushering in an era where interconnected devices and intelligent data exchange redefine the landscape of industrial control and monitoring.
Advancements in SCADA software and hardware form the backbone of this evolutionary journey. From more intuitive Human Machine Interfaces (HMIs) to the incorporation of cloud-based solutions, the future promises a SCADA ecosystem marked by enhanced user experiences and unprecedented flexibility. The interplay of software sophistication and hardware innovation paves the way for a SCADA landscape that adapts to the dynamic needs of modern industries.
One of the most transformative trends on the horizon is the integration of predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) into SCADA systems. This infusion empowers SCADA to not only monitor and control processes in real-time but also to anticipate potential issues, prescribe proactive solutions, and continually optimize operations. As industries embrace these future trends, SCADA systems are poised to become not just guardians of efficiency but catalysts for innovation in the ever-evolving landscape of industrial automation. This section explores the exciting frontier of these trends, shedding light on the transformative potential they hold for the future of SCADA systems.
Conclusion:
In the context of modern plant automation, SCADA systems act as orchestrators, seamlessly integrating the diverse elements of control, monitoring, and data acquisition. Throughout this exploration, the role of SCADA systems proves pivotal, offering real-time insights, improving efficiency, and fostering resilience in the industrial landscape. Serving as guardians of precision, reliability, and proactive decision-making, SCADA ensures the smooth operation of machinery and processes. However, in the continually evolving technological landscape, the journey persists, evolving with time. The significance of staying informed about advancing technologies cannot be emphasized enough. As we progress into a future characterized by IoT integration, sophisticated software, and the integration of predictive analytics and artificial intelligence, the role of SCADA systems gains further prominence. It is not merely about maintaining relevance; it is about embracing innovation and harnessing the transformative potential of technology.
This exploration underscores the imperative for industries to invest in robust SCADA systems. These investments transcend mere operational enhancements; they become strategic imperatives for fostering improved efficiency and heightened competitiveness. The dynamic interplay of SCADA systems with evolving technologies propels industries toward a future where automation is not just a tool but a philosophy, shaping the very fabric of industrial landscapes. Therefore, as industries chart their course in the digital era, the call to invest in SCADA systems echoes as a clarion, beckoning them to not only adapt but to thrive in the ever-accelerating pace of technological evolution.