PAL Robotics

About: Francesco Ferro - CEO and co-founder
Francesco Ferro is the CEO and co-founder of PAL Robotics, one of the top service robotics companies in the world, and a euRobotics asibl Board Director. He received a BSc + MSc degree in Telecommunications Engineering at Politecnico di Torino in 2002 (Italy), a Master at ISEN (Lille, France) and an Executive MBA at the University of Barcelona (Spain) in 2011. Since 2004, he develops cutting-edge humanoid service robots at PAL Robotics.
1. Pal Robotics is going to participate in Global Robot Expo in Madrid from 18th to 20th April 2018. What would be your key highlights about this mobile manipulator robot at the event?
It is clear that collaborative robotics is the upcoming trend that is about to reshape the industry. The way they can work hand by hand with human workers, and increase efficiency while ensuring safeness for operators is promising. That is why the interest in the market of robots that are qualified as “collaborative” has rapidly grown.
One big advantage of the collaborative robot TIAGo is the integration of smart mobility with manipulation and perception in a single system, focused on human robot interaction. Most platforms in the market do have sensors to detect the environment and arms for manipulation, but have a fixed workspace that obliges workers to place the pieces near the robot. TIAGo’s autonomous navigation enables it to operate wherever the worker needs it or go where the needed material is.
The possibilities in terms of flexibility are endless with such dynamic tool. TIAGo’s day is not limited to one single task. Workers can easily command the robot, schedule diverse tasks and reschedule the planning on the go, switching from one task to another. Even if workers aren’t skilled at programming, TIAGo can be controlled with a user-friendly interface or even learn movements easily with hand guiding methods.
This is important because dynamism is key to enable the “Factory of the future”, where manufacturing areas will be continuously in transformation. For that matter, an open configuration of robotic agents, the possibility of plug-and-play sensors, end-effectors, even software applications, is also highly valuable.
2. Of all the robots (REEM, REEM – C, StockBot, TIAGo, TIAGo Base, TALOS), which one is the most advanced robot from the functionality point of view?
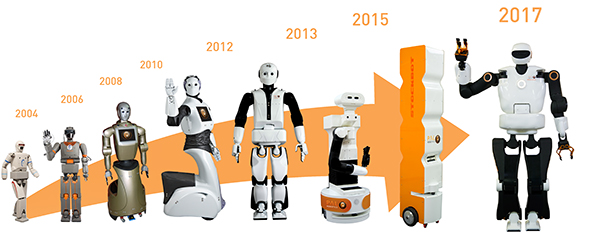
Since 2010 our robots have been diversifying and adjusting to different scenarios where each of them could take a relevant role. So it depends on the context in which we evaluate each of the robots to decide which one would be the most advanced one.
For instance, if we talk about humanoids interacting with the environment in a safe way, TALOS would be outstanding. It is a fully electrical humanoid robot with fully torque sensor feedback in all joints. Standing at 1.75m high, it can walk up to 3Km/h and lift 6 Kg with each arm fully extended.
TALOS is one of the most powerful bipeds of its kind, able to respond to any external stimulus in a fast and precise way. The humanoid robot has been designed to perform heavy, non-ergonomic actions that can be dangerous for factory workers in Industry 4.0.
We develop other robots that have a different architecture from the bipedal humanoids to best adapt to its functionality. An example of this is TIAGo: its diverse configurations make the robot suitable for helping in both industrial and domestic settings. TIAGo base itself is also demanded for industry as an autonomous robotic vehicle that intelligently carries goods from one place to another.
Another example is StockBot: this platform is successfully taking inventory in stores and warehouses autonomously. The robot is in various retail stores in Europe having everything that moves or changes of place under control, and provides valuable information that improves stock management and optimization.
3. Could you please describe how ‘REEM: Full-size humanoid service robot’is different from other robots? (Special points compared to your competitors)
REEM is the flagship service robot for events and public spaces, such as shopping malls, museums, airports, etc. It is a human-sized robot (1.70m tall) that can be a dynamic information point, guide, entertainer, or even provide logistics or surveillance services. REEM can speak in many languages, recognize faces, make gestures, show information on its touchscreen, and move around with a mobile base. REEM also has a base behind where it can carry luggage or goods.
REEM is usually rented by companies when they participate in fairs, exhibitions or events since it attracts a lot of people and it becomes a very powerful marketing tool - REEM has been to more than 100 events so far. Some universities and innovation labs use REEM for research purposes too.
4. Where is Pal Robotics seeing the greatest uptake of robots?
The potential of robotics can widely improve our day to day routine and enhance our quality of life; this is what moves us to push the limits of robotics with our platforms. We especially think of two big areas: Ambient Assisted Living and Industry 4.0.
In Industry 4.0 robots should undertake tasks that are risky or dangerous for people, so humans are prevented from suffering any health injury that conditions their life from that moment on. The idea of human-machine collaboration pursues the goal of having the fullest efficiency while adding value to the worker’s role. As humans, we have extraordinary capabilities that enable us to do higher valued work that is more dynamic and even enjoyable than a repetitive movement for many hours a day.
Research in Ambient Assisted Living with robots shows the high benefits that it has for old people to have a robot accompanying them in their daily routine. Gaining independence in their own life or feeling more optimistic when facing the challenges related to elderly are some of the conclusions we reached in some EU research projects after successful pilots, such as SACRO and EnrichMe.
5. Can you please share your view on the best, effective human-robot interface?
From my point of view, natural language is the best human-robot interface. The robot using its own sensors to understand commands and orders from humans just as we do. Natural language makes it extremely easy for people to command the robot and lowers the entry barrier so much that anyone without technical knowledge can get to benefit from the robot. It is still a challenging field that the robotics community is still perfecting this promising field, there’s still room to progress here from a technical point of view.
6. Please give examples of the different applications that your robots provide for the automation industry?
TIAGo base carries goods from one point to another inside industrial settings. The base autonomously navigates finding the best route, and is constantly aware of any change thanks to the integrated sensors, guaranteeing safeness and effectiveness. TIAGo base’s upper area can be customized and adapted to the diverse equipment it has to work with.
TIAGo combines autonomous navigation with smart perception, manipulation abilities, and Human-Robot Interaction skills to easily adapt to diverse industrial tasks. The robot becomes a dynamic tool that has enough flexibility to change from one task to another under the worker’s commands, which also allows the possibility of task scheduling.
Mobile pick and place, assembly tasks, courier, sealing or gluing are some examples of tasks that TIAGo can do. Its modular structure enables the robot to easily integrate and exchange different tools, sensors or end-effectors to best accomplish with any specific need. The person can intuitively control the robot through tablet applications, voice commands or remote teleoperation. TIAGo can also be taught how to perform new movements by easily guiding its hand without needing technical knowledge.
StockBot exhaustively controls inventory in warehouses. The platform autonomously navigates through the corridors while detecting all items, using RFID technology complemented with vision. StockBot can work both with people and without people around, benefitting from the same autonomous navigation system than TIAGo base. After the route is completed, StockBot provides a list of what is in the warehouse and a 3D map with all items’ location.
TALOS is being used for research in introducing humanoid bipedal robots in manufacturing. Its payload and arms architecture enables it to nimbly manipulate heavy tools that can weight up to 6Kg. Drilling or riveting are some examples of the tasks that the robot can perform. Its bipedal structure also enables the TALOS to adapt to uneven grounds and climb stairs, widening its workspace.
7. Do you really think robots will replace human labor force taking away their jobs in the coming future?
What, if we see it, the other way around: nowadays I actually see some people stealing jobs from robots. Some tasks performed by humans are extremely repetitive and tedious, even dangerous sometimes. Health suffers when these tasks are performed for a long period of time, or in unergonomic positions.
I believe robots should undertake some of the tasks to prevent people from suffering any harm or injury, which in the end have an impact in the whole life of a person, so I see an advantage for people here. All industrial revolutions have reshaped the market, and opened new fields. There are numerous jobs that appeared with cars or with computers. I believe that if it is done for the benefit of everyone, it is good that some jobs are left to robots.
