Types Of Industrial Printed Circuit Boards
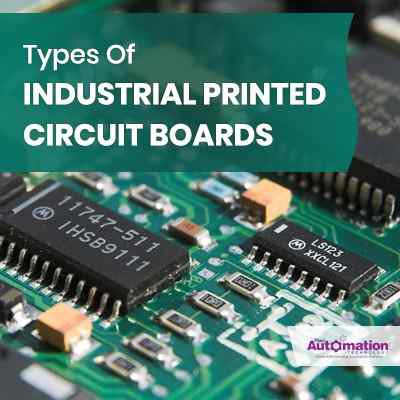
A thin board of composite epoxy, fiberglass or other laminate material is referred as PCB, an acronym of printed circuit board. The circuit board contains tracks, lines and paths, to electrically connect different electronics components. The electronic components are mechanically supported and electrically connected by PCB, using conductive pathways, signal traces or tracks, etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conducive substrate. You will find components such as capacitors and resistors soldered onto some PCBs.
An etched wiring board or printed wiring board (PWD) is more correctly defined when the board has no circuit elements such as resistors, capacitors or active devices, but has only copper tracks and features. As the distinction between circuit and wiring has become blurred, the usage of the term PWB has generally fallen by the wayside for many people. Used both for assembled and bare boards.
Different Types Of Printed Circuit Boards
Let’s look in and explore the features of different types of printed circuit boards.
Single sided, double sided and multi layered are the three ways used for the construction of PCB. Using two different methodologies like, hole technology and surface mount technology, the required components are connected electrically with the PCB board. Based on your requirements related to project, you can choose any PCB.
A) SINGLE SIDED PCBs
This type of printed circuit board usually contains one layer of base material/substrate. The single sided PCBs are mostly used in simple electronics as they don’t involve complex circuitry, and are an ideal choice for the beginners. The cheap cost and easy availability makes these PCBs an ideal choice for mass production.
Widely used in applications including cameras, calculators, stereo components, vending machines, printers, surveillance, coffee makers, LED lighting, solid state drives, packaging equipment, relays, timing circuits, radio and stereo equipment, sensor products and power supplies.
B) DOUBLE SIDED PCBs

This printed circuit board is much similar to single sided PCBs, with one exception that they contain copper material on both sides of the substrate material. The components on these PCB boards are connected using two different technologies, i.e. hole and surface mount.
Featuring moderate level of complexity, they are widely used in a range of applications including LED lighting, convertors, HVAC system, industrial controls, traffic control system, regulators, automotive dashboard, power conversion, amplifiers, control relays, power supplies, instrumentation, UPS power system, PC hard drives, vending machines, printers, line reactors, phone system, and test and monitoring equipment.
C) MULTILAYER PCBs

Compared to the double sided PCBs, these multilayer PCBs are more complex and come with a combination of single and double sided boards. In order to provide protection, a piece of insulation is placed between each board, that prevents components from burning in case of excess heat production.
These multi layer PCBs are widely used in number of applications including data storage, GPS technology, satellite system, file servers, weather analysis systems, mobile phones, computers, signal transmission, heart monitors, cell phone repeaters, atomic accelerators, X ray equipment, fiber optic receptors, central fire alarm systems, space probe equipment, cell phone transmission.
Limitations :
Before you pick a multilayer PCB, you need to consider the overall project cost as the high manufacturing cost is an important factor in its selection. A major constraint would be its manufacturing time, when compared to single and double layer PCB and also it requires more complex repair at the time of permanent damage or certain loss.
D) RIGID PCBs

The rigid PCBs are used commonly in electronics, that provide strength to the circuits, prevent them from twisting, make them rigid. An ideal example of rigid PCBs would be the computer motherboard, that is composed of rigid substrate material. Different software such as Proteus, EasyPC, and Altium can be used to design these PCBs.
Found in low cost products such as electronics, toys, gadgets, solid state devices, and desktop devices.
E) FLEXIBLE PCBs
Based on needs and requirements, they are flexible and can transform or flex into any shape. In contrast to rigid PCBs, these flexible PCBs, also referred as Flex Circuit use plastic material. These PCBs mostly use polyester, polymide or PEEK (Polyether ether ketone).
In cases where flexibility, less weight, and space saving are top priorities, the flexible PCBs widely replace rigid PCBs. The computer keyboard is a very common example of flexible board. Many consumer electronics like cameras, personal entertainment devices, automotive industries, and exercise monitors calculators, are incorporated with flexible circuits.
F) RIGID FLEX PCBs

When number of flexible PCBs are combined with range of rigid layers, the rigid flex PCBs are manufactured. The less space and minimum weight required to build a whole circuit makes these PCBs an ideal choice for most of the applications. Widely used in medical applications such as pacemakers and automobiles, aerospace systems, digital cameras, military weapons and cell phones.
G) HIGH FREQUENCY PCBs

These are slightly different in terms of materials used and construction point of view from traditional PCBs. They can transmit signals over one GHz. Before choosing high frequency PCBs, dielectric constant, dielectric thickness, and power dissipation are few things to take into consideration.
In number of applications like advanced communications systems and industrial and medical applications, these high frequency products can be observed. Similarly, for better signal transmission, cell phones, RF remote control, GPS receiver, ZigBee make use of high speed products. A true example of high speed circuits are airborne and ground based radar systems.
H) ALUMINUM BACKED PCBs
Also referred as metal base PCB, consists of a copper clad laminate and thin dielectric thermally conductive and electrically insulated layer, that is laminated between metal base and copper foil. Based on their construction and design, there are number of types of aluminum PCBs, used in many applications.
- Flexible aluminum PCBs
- Hybrid aluminum PCBs
- Multi layer aluminum PCB
- Through hole aluminum PCB
Used in LED applications, automotive and radio frequency industries.
| Also Read: The Role of Printed Circuit Boards in Industrial Automation |
Market Insights:
With a CAGR of 4.3% from 2019 to 2024, the global PCB market is expected to reach an estimated $89.7 billion by 2024. An increasing demand for PCB in advancement in automotive electronics, communication industry, growth in connected devices, are the major growth drivers for this market.
With opportunities in communications, consumer electronics, computer/peripherals, automotive, industrial, military/aerospace industries, the future of PCB looks quite promising.











