Top Global PCB Manufacturers | An Overview of Printed Circuit Boards

The demand for Printed Circuit Board (PCB) market looks promising as it is extensively used in various industries such as communication, automotive, and computer/peripheral industries.
PCB Market - Overview
According to Energias Market Research, the global Printed Circuit Board (PCB) market was valued at 63.1 billion in 2017 and is expected to reach USD 76.9 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 3.1%.
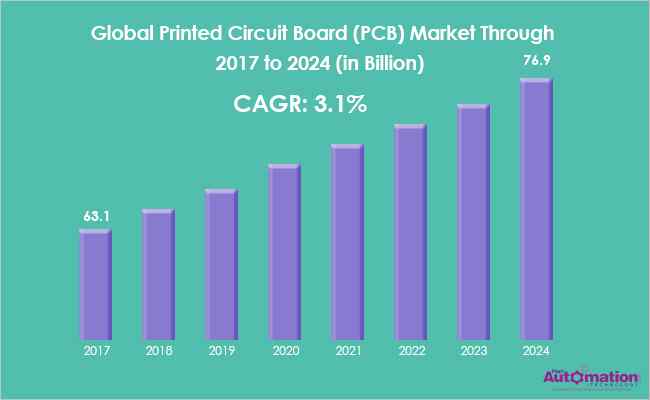
Image: Global Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Market 2017-2024

Factors Driving the Growth of PCB Market:
There are a wide variety of factors that are liable for the growth of the PCB market. They are:
• Growing demand for wireless devices
• Increasing adoption of automation in various end-user industries
• Rising demand for flexible circuits
• Increasing miniaturization of devices
• Surging need for more efficient interconnect solutions
|
Also Read: Industrial Electronics: Powering the Future of Manufacturing |
Introduction to PCB:

Image: Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
A Printed Circuit Board or PCB is used to connect electrical components using tracks instead of wires. To fix the electronic components in position, holes are drilled on the board. They are then soldered and are connected through copper tracks forming a circuit. The board and the components together are known as a PCB Assembly. (or Printed Circuit Board Assembly)
Generally, PCBs are used to electrically connect the components and provide a base on which the entire system can be integrated. To pass current to the proper components, PCB uses extremely thin copper tracks. These thin copper tracks are threaded across a substrate, which is usually either a thin sheet of phenolic resin-infused paper, or an epoxy resin-infused fiberglass mat.
In addition, a single printed circuit board can hold up to sixteen layers of these conductive sheets glued together. The small silver dots on the PCBs are solder points that link through-hole components on the other side.
| Also Read: The Role of Printed Circuit Boards in Industrial Automation |
Designing part of the PCB is the most toughest part than manufacturing it. While designing a printed circuit board, a wide range of factors need to be considered:
• Components must be properly mapped
• Distance between copper tracks and components need to be placed correctly so that current does not jump
• Track widths must match with the frequency of the passing current
In addition, PCB engineering requires more time and effort as it is a highly specialized craft, and layout is often the most expensive aspect of PCB production.
How is A Printed Circuit Board Manufactured?
To manufacture a Printed Circuit Board, initially, the electronic schematic diagram needs to be prepared using Computer Aided Design (CAD) software. With the assistance of schematic diagram, the PCB prototype is developed using Computer Aided Manufacturing Software technology.

Materials that are used for manufacturing PCBs are FR4, FR4 High Temperature Polyimide, Nelco, Rogers, GeTek, Arlon, Alumina, Ceramic, Bakelite, FR1, CEM1, and CEM5. The surface of the board is coated with a layer of copper. The thickness and size of the board depends upon the requirements of the circuit.
After this, the circuit diagram is printed on the board using photosensitive coating. To form copper tracks (traces), the unwanted copper is engraved out from the board. This procedure is called photoengraving.
Connecting traces can be developed using two common methods. They are:
a) PCB Milling - This method is a mechanical system where unwanted copper is removed with CNC machines.
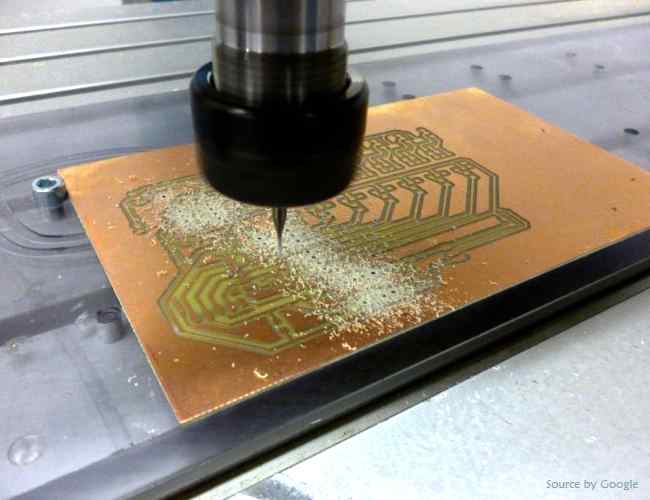

Image: PCB Milling
b) Silk-Screen Printing - In this process, special ink that is etch-resistant used to cover the areas where the copper traces have to be made.
Image: Silk-Screen Printing
Once the board is ready with copper traces, holes are drilled into the board to assemble electrical and electronic components. Drilling process is carried out using special Tungsten Carbide drill bits or laser. Deploying electroplating process, holes are filled with hollow rivets, which helps to form an electrical connection among the various layers.
The next step involves the coating of the entire board, except holes and pads, with masking material. The masking materials used for this purpose are lead solder, lead free solder, OSP (Entek), deep/hard gold (electrolytic nickel gold), immersion gold (electro less nickel gold - ENIG), wire bondable gold (99.99% pure gold), immersion silver, flash gold, immersion tin (white tin), carbon ink, and SN 100CL, an alloy of tin, copper, and nickel.
The final step is screen-printing, where the text is printed on the PCB.
Assembling of PCB (PCB Assembly)
Once the board is ready , PCB Assembly involves the assembling of components and addition to the surface as per the electrical schematic diagram. Some of the common assembly techniques used are '-mount construction' and 'through-hole construction'. Sometimes, a combination of these two techniques is also used for assembly.
Testing Of PCB
Testing of PCB must be carried out before the delivery of Printed Circuit Boards. They are tested to find out 'Short' and 'Opens' that could lead to a non-functioning of the board.
Here, 'Short' refers to the existence of an undesired connection
'Open' indicates that two points that should have been connected appear unconnected
These kind of errors needs to be checked/rectified before the assembly of PCB.
Types of Printed Circuit Boards
There are three types of Printed Circuit Boards. They are:
a) Single Sided Board
b) Double Sided Board
C) Multi Layered Board
a) Single Sided Board
Single sided boards contain a single layer of substrate, i.e. all electrical components and parts are fixed on one side and copper traces on the other side.
Image: Single Sided Board
b) Double Sided Board
Double sided boards are the most commonly used boards, where both electrical parts and components are attached to both sides of the substrate. Double-sided Printed Circuit Boards usually use through-hole construction for assembly of components.
Image: Double Sided Board
c) Multi Layered Board
As the name implies, Multi Layered Board consists of various layers of substrate separated by insulation. Most common multilayer boards are: four layers, six layers, eight layers, and 10 layers. The total number of layers that can be manufactured can exceed over 42 layers.

Image: Multi Layered Board
These types of boards are used in extremely complex electronic circuits.
Uses of PCB:
Printed Circuit Boards (PCB) can be found in all electronic circuits, cell phones, battery-operated toys, TVs, music players, automobiles, computers, game-consoles, alarm systems, ovens, washing machines, coffee machines, and aircraft etc. There's virtually no electronic device that can't be built using PCBs. PCBs can also be found in military, medical and industrial components.

Pros of using PCB:
a)Easy Maintenance
Maintaining the printed circuit boards is much easier as the components are fixed rigidly. As the design of the board is simple, the capability to maintain is easy.
b) Prevents Short-Circuits
The printed circuit boards depend on the embedded copper tracks that are extremely effective at preventing issues with a short-circuit.
c) Great for reproducing
PCBS can be reproduced with exact same design and specification. As these boards are printed from a computer, it would be easy to replicate the board as many times as necessary.
d) Ease of Repair and Diagnostic
It will be easy to check and replace the particular failure components, in case of any damage. Because the electronic components and their polarities on a properly designed, printed circuit boards are clearly labeled on the board.
Why these Ubiquitous Printed Circuit Boards are Usually Green?
If we observe, most of the printed circuit boards resemble green. It indicates that it's made from glass-epoxy which is naturally green. The greener part is the outer covering of resin called the solder mask or solder resist.
The solder mask (which is green color) is applied for safety reasons, for preventing eventual short circuits, protecting from moisture, dust etc. The solder mask can also come in various colors such as yellow, red, blue, black, and white.
Top Global PCB Manufacturers
Here we have listed out the top Global PCB Manufacturers in the world:
• FLEX Ltd
• Eltek Ltd
• SCHMID Group
• Corintech Ltd.
• ES & S Solutions GmbH
FLEX Ltd is one of the third largest global electronics manufacturing service company. This company offers a wide range of electronic design services including PCB design, microelectronics, robotics, and more.
Eltek Ltd. is one of the renowned manufacturers of advanced PCBs for sophisticated electronic products. This company's products are used in some of the world's most advanced electronics including aerospace, defense, and medical applications.
SCHMID Group:
SCHMID Group has been the recognized technology leader in the PCG industry for over 50 years. The company is known for its excellence in the areas of metallization, surface and resist technology. This company follows standardized technologies and customized solutions to implement market demands and customer's requirements appropriately.
Corintech Ltd.
Corintech Ltd provides high quality and competitive PCB assembly services. The company remains on the cutting edge of technology by continually advancing in new hardware. Corintech delivers quality products using all assembly processes.
ES&S Solutions GmbH
ES & S Solutions GmbH has been offering tailor-made cable and adapter solutions, printed circuit boards and their equipment for more than 25 years.