The Best Buying Guide for Selecting the Right Industrial Sensor

An optoelectrical, electronic or electrical device that’s composed of sensitive materials or specialty electronics for determining if there is any presence of a particular entity or function. Many such types of industrial sensors are available including those for detecting a physical presence such as flame, leaks, metals, levels, or gas and chemicals, among others. Few sensors are designed to sense physical properties such as temperature, radiation or pressure, while others can detect proximity or motion. Depending on the application, they operate in a variety of manners and may include electromagnetic fields, or optics, among others.
Types of Industrial Sensors
Depending on the applications, material used in sensor, input signal, conversion mechanism, production technologies or sensor characteristics such as accuracy, cost, or range, the industrial sensors are generally classified into many types. A few of them are -
• Proximity sensors
• Vision sensors
• Ultrasonic sensors
Choosing the right proximity sensors
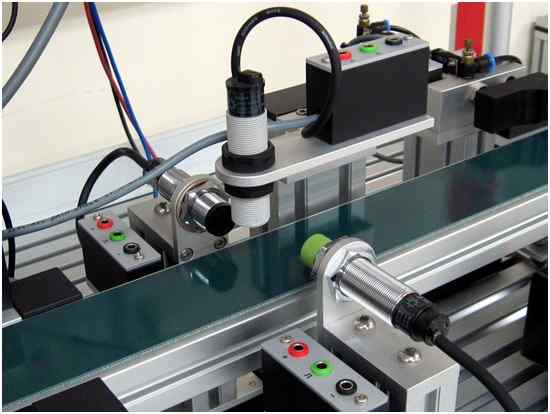

Proximity sensors, also known as detectors are electronic devices that are used to detect the presence of nearby object through non-contacting means. Hence, they are used in several industries, including robotics, manufacturing, semiconductor, and many more.
Types of proximity sensors
As per the working principles, the proximity sensor can be divided into -
Inductive proximity sensor
The sensor head in an inductive proximity sensor is an inductive coil with a ferrite core. Hence, it can only be used to detect metals. These inductive sensors are used in machines for the textile industry, assembly lines, machine tools, and the automotive industry. They are useful in detecting metal parts in harsh environments and when it's necessary to check parts that move quickly.
Capacitive proximity sensor
The sensor head in a capacitive proximity sensor is a circular plate electrode, whereas another polar plate is the object itself. This industrial sensor cannot only detect metals, but also nonmetallic objects or liquids. The capacitive sensors are found on packaging lines, packaging installations, and when filling levels are measured through glass walls or plastic.
Magnetic induction sensor
It's also known as "Hall proximity sensor" as it's working principle is similar to that of the Hall effect i.e. the signal outputs when the magnetic objects approach the Hall switch. Besides, it's mainly used to judge whether the cylinder is retracted or pushed to the specific position.
Special proximity sensor
We need to use the fiber optic proximity sensor or pneumatic proximity sensor, when detecting in some narrow space or harsh working environments, such as humidity, high temperature, large disturbance or explosive environment with a high precision requirement. However, these sensors are quite expensive.
How to choose a proximity sensor?
Before choosing a proximity sensor, we have to know a few important things about it.
A) Detection object
When detecting metals, the inductive proximity sensor should be selected in priority, whereas the capacitive proximity sensor should be selected in priority when detecting nonmetallic materials and the magnetic induction proximity sensor should be selected in priority for detecting magnetic signals.
B) Dimension
According to the actual application occasions and situations, the dimension shall be selected. The most commonly used dimension of the proximity sensor is the cylindrical thread shape like the M12 series.
C) Detection Range
The selection of detection range shall be determined by needs, but the detection distance of the same proximity sensor is not constant. It's related to the material, size and movement directions of the objects under test.
D) Shielded or unshielded
The biggest action distance (related to diameter) can be achieved with the unshielded proximity sensor. The sensor head must be kept at a certain space with the surrounding metal to avoid the influence of the metal surrounding the proximity sensor. Whereas the shielded proximity sensor can be flush mounted inside the metal because of the inside special shielding effect.
E) Output Signal
The AC proximity sensor outputs the AC signal, while the DC proximity sensor outputs the DC signal. The DC output signal can be further divided into PNP output and NPN output. The load current shall be less than the output current of the proximity sensor.
Choosing the right vision sensors

The vision and imaging sensors/detectors are electronic devices that identify the presence of objects /colors within their fields of view. This information is then converted into a visual image for display.
These are products that contain video camera, display and interface, and computer processor to automate industrial processes and decisions. The vision sensors are also referred to as vision systems or machine vision. These are commonly used for measurement, pass/fail decisions, and other observable characteristics relating to product quality. It’s called a smart camera when the camera has an integral processor.
Types of vision sensors
The vision sensors come in two different types and can be adjusted for various purposes.
Orthographic projection-type
In this type of vision sensor, the field of view of orthographic projection-type is rectangular. They are well suitable for close-range infrared sensors, or laser range finders.
Perspective projection-type
In this type of vision sensor, the field of view of perspective projection-type is trapezoidal. They are well suitable for camera-type sensors.
How to choose a vision sensor?
Application requirements along with technology for automated inspections are constantly evolving. When selecting a vision sensor, some of the important features to consider are lighting, development environment, and modularity.
A) Integrated Lighting
Few conditions such as factory environments and space constraints can make it complex to achieve proper lighting conditions. Such conditions can be problematic for vision sensors as they rely on even, diffuse lighting to fixture parts and execute robust inspections with contrast, brightness, and pixel count tools. Generally, the vision sensors come with integrated lighting and if required can be connected to additional external lighting. Selecting a vision sensor with built-in lighting saves money on mounting fixtures and external illumination.
B) Standardized Set-Up Environment
Every novice user should be able to easily set up, configure, and install a vision sensor. Apart from the current inspection needs, future applications that may require more powerful and flexible vision systems need to be considered when selecting a vision sensor. A reliable communication link to other factory automation equipment and fast processing are essential.
C) Flexible, Modular Design
To achieve image resolution, optimal FOV, and part illumination it can be difficult to mount a vision sensor in the precise location. The inspections and run-time can be achieved quickly with vision sensors with small form factors, which regulate into any space and can be configured for in-line and right-angle mounting installation. The modular designs make optical paths and cable routing easier and allow users to change optics, lenses, and lights in the field for quick line changeovers or application modifications. The models with autofocus lenses remove the need to manually refocus or adjust the mounting height.
Choosing the right Ultrasonic sensors
An ultrasonic sensor measures the distance of a target object by emitting ultrasonic sound waves. The reflected sound is converted then into an electrical signal. The ultrasonic sensors are used primarily as proximity sensors. They can be found in anti-collision safety systems, automobile self-parking technology, robotic obstacle detection systems, as well as manufacturing technology. The ultrasonic sensors are also used as level sensors to detect, regulate and monitor liquid levels in closed containers. These, in particular, have enabled the medical industry to identify tumors, produce images of internal organs, and ensure the health of babies in the womb.
Types of Ultrasonic sensors
Currently, there are four major different types of ultrasonic sensors.
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
A special type of sonic transducer is used for the reception and alternate transmission of a sound wave. The sonic waves are emitted by the sonic transducer, which is reflected by an object and after this emission, this sensor then switches into receive mode. The total time which is passed between emitting and receiving of sound wave and distance of an object from the sensor is inversely proportional to each other. It’s only within the detection area that the digital output is possible or sensed. The sensing range can be adjusted with the sensor’s potentiometer.
Ultrasonic 2 Point Proximity Switches
The ultrasonic 2 point proximity switches consist of 2 points for switching. Hence, it’s called 2-point proximity switches. Except for the 2-touch set up key, it’s almost similar with the standard sensor. This function is called Tech-in function.
Ultrasonic Retro-reflective Sensors
Its operation is similar to the ultrasonic proximity sensor. It only differs in the distance between sensors to the reflector, as it’s measured by measuring the propagation time. In this Ultrasonic Retro-reflective Sensor, the reflector could be used as the stationary object and by adjusting the potentiometer resistance within ultrasonic sensor, the sensing distance could be adjusted.
How to choose an Ultrasonic sensor?
A) Mode
The first and foremost thing one needs to do is check the mode of the ultrasonic sensor. When you are using the ultrasonic sensor, there are different modes that can be used. Detection can be possible with the mode that the ultrasonic sensor is using. A good quality ultrasonic sensor should use a mode that is easy to detect an echo.
B) House of ultrasonic sensors
The second factor that you should consider is the house of the ultrasonic sensors. The housing of the sensor plays an important role in ensuring that there is easy mounting of the sensor. Different sensors have different housing. Hence, you need to be cautious when you are choosing an ultrasonic sensor. There are various sensors that can be fixed in different positions. It’s important that you select a sensor that has the right house. Remember that a good housing of the ultrasonic sensor should have strong metal protection that will have the ability to resist tough conditions. Moreover, when you need to reduce the sensors housing, you can also use a plastic house. The housing of the sensor should be chemically resistant and be able to prevent corrosion.
C) Output Type
When you are choosing an ultrasonic sensor, the output type of the ultrasonic sensor will help you. There are ultrasonic sensors that have switch point and analog endpoints. The push buttons that are used by the ultrasonic sensor is very important. Hence, when you are looking for an ultrasonic sensor, you need to carry out your basic research. A good sensor should have the ability to provide you with relative solutions that will meet your needs.
D) Distance
Covering a considerable amount of distance should be the superior quality of a good sensor. The distance should be able to cover a range of around 10 to 10,000mm. When you are choosing a sensor, the dead bands that the ultrasonic sensor has should help you. This will help in selecting a good sensor that will match your needs.
When you are selecting an ultrasonic sensor, the dead bands that the ultrasonic sensors possess should help you. This will help you in choosing a good sensor that will match your requirements.











